Mew Forest
I'm stuck on working with your last example. What should I change to pause my worker until user type something in my gui?
Martin Fitzpatrick
Normally if your worker will be waiting a long time you should just stop and start a new worker later. But if you do want it to wait, you can put it in a wait loop (whileself.waiting==True: time.sleep(0.1)) and update the value of self.waiting with a signal from outside.
Hampus Nasstrom
I've been trying to implement this but I really don't understand how to "update the value of self.waiting with a signal from outside". Tried defining the signal in the main window by adding a class:
class MainSignals(QObject):
wait_signal = pyqtSignal(bool)
and then add self.signals = MainSignals() in the init of the main window.
I then send the parent (the main window) to the worker but when I connect to the signal with self.parent.signals.wait_signal.connect(self.set_wait) I get the error: TypeError: connect() failed between MainSignals.wait_signal[bool] and set_wait()
Packaging Python Applications with PyInstaller by Martin Fitzpatrick — This step-by-step guide walks you through packaging your own Python applications from simple examples to complete installers and signed executables.
Martin Fitzpatrick
Have a look at this example. It uses methods on the worker to update the values, which are then connected to the signals from the buttons.
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (
QWidget, QApplication, QProgressBar, QMainWindow,
QHBoxLayout, QPushButton
)
from PyQt5.QtCore import (
Qt, QObject, pyqtSignal, pyqtSlot, QRunnable, QThreadPool
)
import time
class WorkerSignals(QObject):
progress = pyqtSignal(int)
class JobRunner(QRunnable):
signals = WorkerSignals()
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.is_paused = False
self.is_killed = False
@pyqtSlot()
def run(self):
for n in range(100):
self.signals.progress.emit(n + 1)
time.sleep(0.1)
while self.is_paused:
time.sleep(0)
if self.is_killed:
break
def pause(self):
self.is_paused = True
def resume(self):
self.is_paused = False
def kill(self):
self.is_killed = True
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# Some buttons
w = QWidget()
l = QHBoxLayout()
w.setLayout(l)
btn_stop = QPushButton("Stop")
btn_pause = QPushButton("Pause")
btn_resume = QPushButton("Resume")
l.addWidget(btn_stop)
l.addWidget(btn_pause)
l.addWidget(btn_resume)
self.setCentralWidget(w)
# Create a statusbar.
self.status = self.statusBar()
self.progress = QProgressBar()
self.status.addPermanentWidget(self.progress)
# Thread runner
self.threadpool = QThreadPool()
# Create a runner
self.runner = JobRunner()
self.runner.signals.progress.connect(self.update_progress)
self.threadpool.start(self.runner)
btn_stop.pressed.connect(self.runner.kill)
btn_pause.pressed.connect(self.runner.pause)
btn_resume.pressed.connect(self.runner.resume)
self.show()
def update_progress(self, n):
self.progress.setValue(n)
app = QApplication([])
w = MainWindow()
app.exec_()
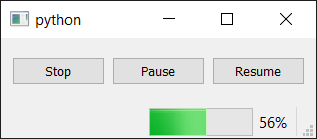
When you run this you'll see a progress bar moving left to right. If you hit pause it will pause, and resume it will restart. If you press stop it will kill the runner (by exiting the loop).
Albert Ang
Thank you for your wonderful example. I have a slight problem in using your example. When user closes the GUI without clicking on the Stop button, the thread seems to continue to run. Can advise on the detection of user's close GUI event and stop all the threads gracefully?
Martin Fitzpatrick
To detect when the app is shutting down you can use the .aboutToQuit signal on QApplication. You can connect this up to your workers stop/kill slot to trigger it on shutdown, e.g.
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
Then to connect the worker
app.aboutToQuit.connect(worker.stop)
If you have many workers, you might prefer to connect this to a handler that will clean up all the workers in one go.
If you have per-window workers, you could also catch the window closeEvent and stop the workers there.
Purchasing Power Parity
Developers in [[ country ]] get [[ discount.discount_pc ]]% OFF on all books & courses with code [[ discount.coupon_code ]]Albert Ang
[quote="martin, post:6, topic:147"]
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
[/quote]
Thank you for your prompt reply! I followed your code with app = QApplication(sys.argv) and app.aboutToQuit.connect(worker.stop) but I got the worker not defined error. As I used your example above which is # Create a runner self.runner = JobRunner() self.runner.signals.progress.connect(self.update_progress) self.threadpool.start(self.runner)
so I tried app.aboutToQuit.connect(runner.stop) but my program gave runner is not defined error. When I run my Python program eg. test.py, do I need to run it with an argument? eg. test.py runner?
Martin Fitzpatrick
The "not defined" error means that there isn't a variable with the name you're using -- that either means you're using the name before it's been defined, or you're using the wrong name.
In this case, when you define the window the runner object hasn't been created yet, so it can't be connected to. The simplest thing to do is to add an extra method on your window to handle this sort of "shutdown" cleanup, e.g.
def shutdown(self):
if self.runner: # set self.runner=None in your __init__ so it's always defined.
self.runner.stop()
...and then you can connect to that method, since it's available as soon as the window is created.
app.aboutToQuit.connect(w.shutdown) # connect to the shutdown method on the window.
Hampus Nasstrom
Hi Martin, I'm sorry I missed you reply after the update to a forum. Thank you so much for the reply! I had implemented something similar where the worker checked by calling a function of the parent but this is more elegant. Really appreciate your website, it really helps me as a PhD student in physics having to implement a bunch of GUIs. Many thanks!
Create GUI Applications with Python & Qt5 by Martin Fitzpatrick — (PyQt5 Edition) The hands-on guide to making apps with Python — Over 10,000 copies sold!

