In Qt (and most User Interfaces), widget is the name given to a component of the UI that the user can interact with. User interfaces are made up of multiple widgets, arranged within the window.
Qt comes with a large selection of widgets available and even allows you to create your own custom and customized widgets.
A Quick Demo: PySide6 Widgets
First, let's have a look at some of the most common PySide widgets. The following code creates a range of PySide widgets and adds them to a window layout so that you can see them together:
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (
QApplication,
QCheckBox,
QComboBox,
QDateEdit,
QDateTimeEdit,
QDial,
QDoubleSpinBox,
QFontComboBox,
QLabel,
QLCDNumber,
QLineEdit,
QMainWindow,
QProgressBar,
QPushButton,
QRadioButton,
QSlider,
QSpinBox,
QTimeEdit,
QVBoxLayout,
QWidget,
)
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Widgets App")
layout = QVBoxLayout()
widgets = [
QCheckBox,
QComboBox,
QDateEdit,
QDateTimeEdit,
QDial,
QDoubleSpinBox,
QFontComboBox,
QLCDNumber,
QLabel,
QLineEdit,
QProgressBar,
QPushButton,
QRadioButton,
QSlider,
QSpinBox,
QTimeEdit,
]
for widget in widgets:
layout.addWidget(widget())
central_widget = QWidget()
central_widget.setLayout(layout)
self.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec()
Run it! You'll see a window appear containing all the widgets we've created.
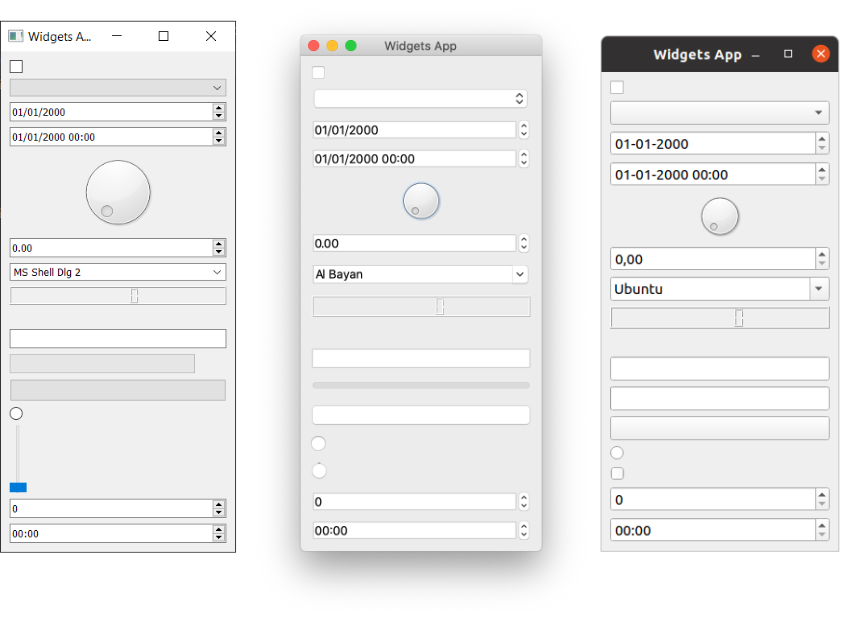 Big ol' list of widgets on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
Big ol' list of widgets on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
Let's have a look at all the example widgets, from top to bottom:
| Widget | What it does |
|---|---|
QCheckbox |
A checkbox |
QComboBox |
A dropdown list box |
QDateEdit |
For editing dates and datetimes |
QDateTimeEdit |
For editing dates and datetimes |
QDial |
Rotateable dial |
QDoubleSpinBox |
A number spinner for floats |
QFontComboBox |
A list of fonts |
QLCDNumber |
A quite ugly LCD display |
QLabel |
Just a label, not interactive |
QLineEdit |
Enter a line of text |
QProgressBar |
A progress bar |
QPushButton |
A button |
QRadioButton |
A toggle set, with only one active item |
QSlider |
A slider |
QSpinBox |
An integer spinner |
QTimeEdit |
For editing times |
There are far more widgets than this, but they don’t fit so well! You can see them all by checking the Qt documentation.
Purchasing Power Parity
Developers in [[ country ]] get [[ discount.discount_pc ]]% OFF on all books & courses with code [[ discount.coupon_code ]]Next, we'll step through some of the most commonly used widgets and look at them in more detail. To experiment with the widgets we'll need a simple application to put them in. Save the following code to a file named app.py and run it to make sure it's working:
import sys
from PySide6.QtCore import Qt
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (
QApplication,
QCheckBox,
QComboBox,
QDial,
QDoubleSpinBox,
QLabel,
QLineEdit,
QListWidget,
QMainWindow,
QSlider,
QSpinBox,
)
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My App")
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec()
In the code above, we've imported a number of Qt widgets. Now we'll step through each of those widgets in turn, adding them to our application and seeing how they behave.
QLabel
We'll start the tour with QLabel, arguably one of the simplest widgets available in the Qt toolbox. This is a simple one-line piece of text that you can position in your application. You can set the text by passing in a str as you create it:
label = QLabel("Hello")
Or, by using the .setText() method:
label_1 = QLabel("1") # The label is created with the text 1.
label_2.setText("2") # The label now shows 2.
You can also adjust font parameters, such as the size of the font or the alignment of text in the widget:
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My App")
label = QLabel("Hello")
font = label.font()
font.setPointSize(30)
label.setFont(font)
label.setAlignment(
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignHCenter | Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignVCenter
)
self.setCentralWidget(label)
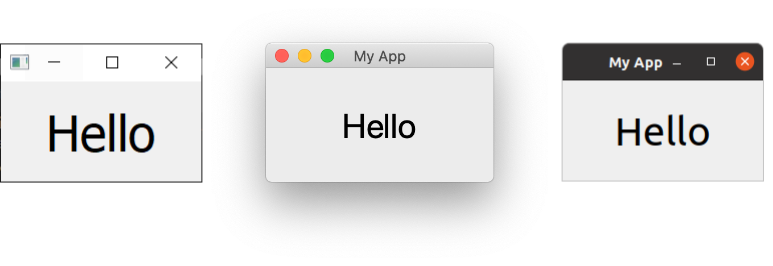 QLabel on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
QLabel on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
Font tip Note that if you want to change the properties of a widget font it is usually better to get the current font, update it and then apply it back. This ensures the font face remains in keeping with the desktop conventions.
The alignment is specified by using a flag from the Qt.AlignmentFlag namespace. The flags available for horizontal alignment are:
| Flag | Behavior |
|---|---|
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignLeft |
Aligns with the left edge. |
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignRight |
Aligns with the right edge. |
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignHCenter |
Centers horizontally in the available space. |
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignJustify |
Justifies the text in the available space. |
The flags available for vertical alignment are:
| Flag | Behavior |
|---|---|
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignTop |
Aligns with the top. |
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignBottom |
Aligns with the bottom. |
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignVCenter |
Centers vertically in the available space. |
You can combine flags together using pipes (|), however, note that you can only use the vertical or horizontal alignment flag at a time:
align_top_left = Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignTop
Note that you use an OR pipe (`|`) to combine the two flags (not A & B). This is because the flags are non-overlapping bitmasks. e.g. Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignLeft has the hexadecimal value 0x0001, while Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignBottom is 0x0040. By ORing flags together, we get the value 0x0041 representing 'bottom left'. This principle applies to all other combinatorial Qt flags. If this is gibberish to you, feel free to ignore it and move on. Just remember to use the pipe operator (`|`).
Finally, there is also a shorthand flag that centers in both directions simultaneously:
| Flag | Behavior |
|---|---|
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignCenter |
Centers horizontally and vertically |
Weirdly, you can also use QLabel to display an image using .setPixmap(). This accepts a pixmap object, which you can create by passing an image filename to the QPixmap class.
Below is an image which you can download for this example.
 "Otje" the cat.
"Otje" the cat.
Place the file in the same folder as your code, and then display it in your window as follows:
widget.setPixmap(QPixmap('otje.jpg'))
 "Otje" the cat, displayed in a window.
"Otje" the cat, displayed in a window.
What a lovely face. By default, the image scales while maintaining its aspect ratio. If you want it to stretch and scale to fit the window completely, you can set .setScaledContents(True) on the QLabel:
label.setScaledContents(True)
QCheckBox
The next widget to look at is QCheckBox(), which presents a checkable box to the user, as the name suggests. However, as with all Qt widgets, there are a number of configurable options to change the widget behaviors:
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My App")
checkbox = QCheckBox()
checkbox.setCheckState(Qt.CheckState.Checked)
# For tristate: widget.setCheckState(Qt.PartiallyChecked)
# Or: widget.setTriState(True)
checkbox.stateChanged.connect(self.show_state)
self.setCentralWidget(checkbox)
def show_state(self, state):
print(state == Qt.CheckState.Checked.value)
print(state)
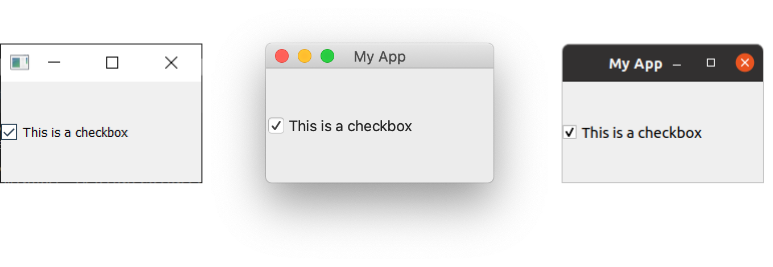 QCheckBox on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
QCheckBox on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
You can set a checkbox state programmatically using .setChecked() or .setCheckState(). The former accepts either True or False, representing checked or unchecked, respectively. With .setCheckState(), you also specify a particular checked state using a Qt.CheckState namespace:
| Flag | Behavior |
|---|---|
Qt.CheckState.Unchecked |
Item is unchecked |
Qt.CheckState.PartiallyChecked |
Item is partially checked |
Qt.CheckState.Checked |
Item is checked |
A checkbox that supports a partially-checked (Qt.CheckState.PartiallyChecked) state is commonly referred to as tri-state, which means the widget is neither on nor off. A checkbox in this state is commonly shown as a greyed-out checkbox and is commonly used in hierarchical checkbox arrangements where sub-items are linked to parent checkboxes.
If you set the value to Qt.CheckState.PartiallyChecked the checkbox will become tristate. You can also set a checkbox to be tri-state without setting the current state to partially checked by using .setTriState(True)
You may notice that when the script is running, the current state number is displayed as an int with checked = 2, unchecked = 0, and partially checked = 1. You don’t need to remember these values, the Qt.CheckState.Checked namespace variable = 2, for example. This is the value of these states' respective flags. This means you can test state using state == Qt.CheckState.Checked.
QComboBox
The QComboBox widget is a drop-down list, closed by default with an arrow to open it. You can select a single item from the list, with the currently selected item being shown as a label on the widget. The combo box is suited to selecting choices from a list of options.
You have probably seen the combo box used for the selection of font faces, or sizes, in word-processing applications. Although Qt actually provides a specific font-selection combo box as QFontComboBox.
You can add items to a QComboBox by passing a list of strings to .addItems(). Items will be added in the order they are provided:
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My App")
combobox = QComboBox()
combobox.addItems(["One", "Two", "Three"])
# The default signal from currentIndexChanged sends the index
combobox.currentIndexChanged.connect(self.index_changed)
# The same signal can send a text string
combobox.currentTextChanged.connect(self.text_changed)
self.setCentralWidget(combobox)
def index_changed(self, index): # index is an int starting from 0
print(index)
def text_changed(self, text): # text is a str
print(text)
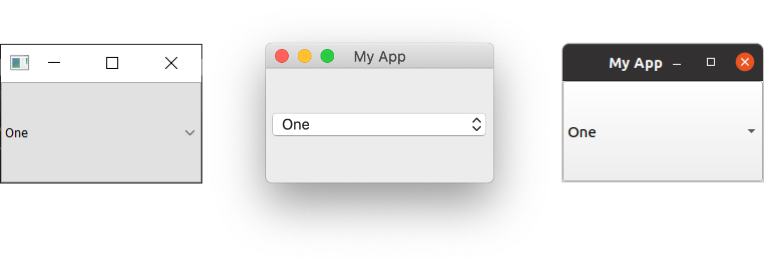 QComboBox on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
QComboBox on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
The .currentIndexChanged signal is triggered when the currently selected item is updated, by default passing the index of the selected item in the list. There is also a .currentTextChanged signal, which instead provides the label of the currently selected item. This signal is often more useful.
QComboBox can also be editable, allowing users to enter values not currently in the list and either have them inserted, or simply used as a value. To make the box editable:
combobox.setEditable(True)
You can also set a flag to determine how the insert is handled. These flags are stored on the QComboBox class itself and are listed below:
| Flag | Behavior |
|---|---|
QComboBox.InsertPolicy.NoInsert |
No insert |
QComboBox.InsertPolicy.InsertAtTop |
Insert as first item |
QComboBox.InsertPolicy.InsertAtCurrent |
Replace currently selected item |
QComboBox.InsertPolicy.InsertAtBottom |
Insert after last item |
QComboBox.InsertPolicy.InsertAfterCurrent |
Insert after current item |
QComboBox.InsertPolicy.InsertBeforeCurrent |
Insert before current item |
QComboBox.InsertPolicy.InsertAlphabetically |
Insert in alphabetical order |
To use these, apply the flag as follows:
Create GUI Applications with Python & Qt6 by Martin Fitzpatrick — (PyQt6 Edition) The hands-on guide to making apps with Python — Over 15,000 copies sold!
combobox.setInsertPolicy(QComboBox.InsertPolicy.InsertAlphabetically)
You can also limit the number of items allowed in the box by using the .setMaxCount() method:
combobox.setMaxCount(10)
For a more in-depth look at the QComboBox take a look at my QComboBox documentation.
QListWidget
Next QListWidget. It's very similar to QComboBox, differing mainly in the signals available and in its on-screen appearance. This one is a box with a list of options rather than a drop-down list:
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My App")
listwidget = QListWidget()
listwidget.addItems(["One", "Two", "Three"])
# In QListWidget there are two separate signals for the item, and the str
listwidget.currentItemChanged.connect(self.index_changed)
listwidget.currentTextChanged.connect(self.text_changed)
self.setCentralWidget(listwidget)
def index_changed(self, index): # Not an index, index is a QListWidgetItem
print(index.text())
def text_changed(self, text): # text is a str
print(text)
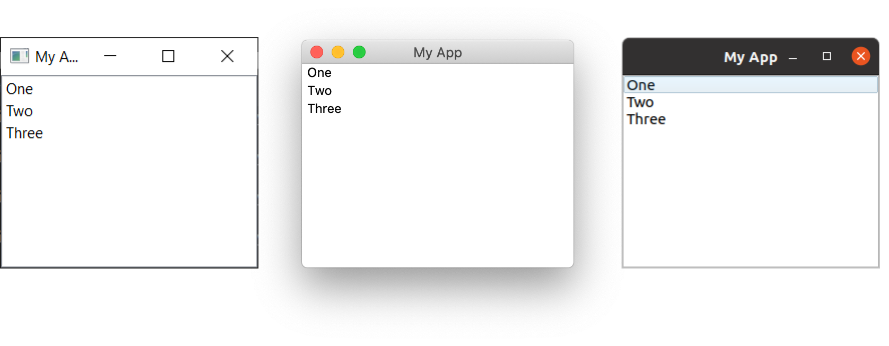 QListWidget on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
QListWidget on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
QListWidget offers a currentItemChanged signal that sends the QListWidgetItem (the element of the list box), and a currentTextChanged signal that sends the text of the item.
QLineEdit
The QLineEdit widget is a simple single-line text editing box, into which users can type input. These are used for form fields, or settings where there is no restricted list of valid inputs. For example, when entering an email address or computer name:
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My App")
self.lineedit = QLineEdit()
self.lineedit.setMaxLength(10)
self.lineedit.setPlaceholderText("Enter your text")
# widget.setReadOnly(True) # uncomment this to make readonly
self.lineedit.returnPressed.connect(self.return_pressed)
self.lineedit.selectionChanged.connect(self.selection_changed)
self.lineedit.textChanged.connect(self.text_changed)
self.lineedit.textEdited.connect(self.text_edited)
self.setCentralWidget(self.lineedit)
def return_pressed(self):
print("Return pressed!")
self.lineedit.setText("BOOM!")
def selection_changed(self):
print("Selection changed")
print(self.lineedit.selectedText())
def text_changed(self, text):
print("Text changed...")
print(text)
def text_edited(self, text):
print("Text edited...")
print(text)
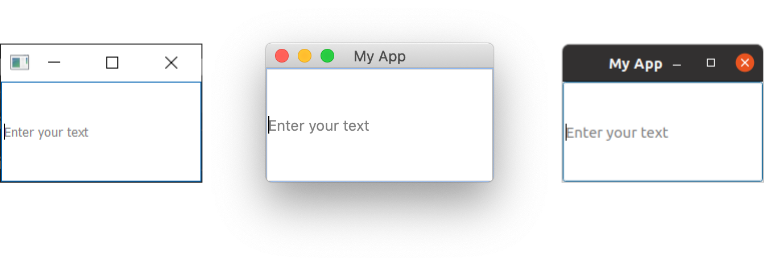 QLineEdit on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
QLineEdit on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
As demonstrated in the above code, you can set a maximum length for the text in a line edit.
The QLineEdit has a number of signals available for different editing events, including when the Enter key is pressed (by the user), and when the user selection is changed. There are also two edit signals, one for when the text in the box has been edited and one for when it has been changed. The distinction here is between user edits and programmatic changes. The textEdited signal is only sent when the user edits text.
Additionally, it is possible to perform input validation using an input mask to define which characters are supported and where. This can be applied to the field as follows:
lineedit.setInputMask('000.000.000.000;_')
The above would allow a series of 3-digit numbers separated with periods, and could therefore be used to validate IPv4 addresses.
QSpinBox and QDoubleSpinBox
QSpinBox provides a small numerical input box with arrows to increase and decrease the value. QSpinBox supports integers, while the related widget, QDoubleSpinBox, supports floats:
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My App")
spinbox = QSpinBox()
# Or: doublespinbox = QDoubleSpinBox()
spinbox.setMinimum(-10)
spinbox.setMaximum(3)
# Or: doublespinbox.setRange(-10, 3)
spinbox.setPrefix("$")
spinbox.setSuffix("c")
spinbox.setSingleStep(3) # Or e.g. 0.5 for QDoubleSpinBox
spinbox.valueChanged.connect(self.value_changed)
spinbox.textChanged.connect(self.value_changed_str)
self.setCentralWidget(spinbox)
def value_changed(self, value):
print(value)
def value_changed_str(self, str_value):
print(str_value)
Run it, and you'll see a numeric entry box. The value shows pre and post fix units, and is limited to the range +3 to -10.
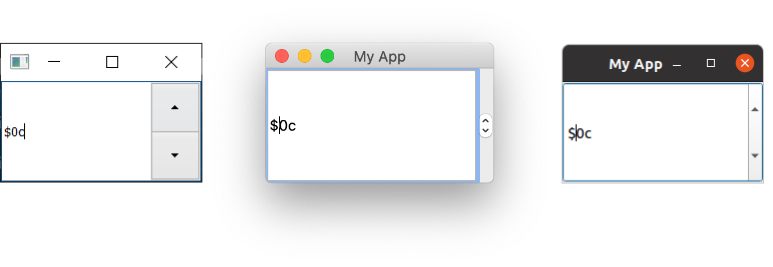 QSpinBox on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
QSpinBox on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
The demonstration code above shows the various features that are available for the widget.
To set the range of acceptable values, you can use .setMinimum() and .setMaximum(). You can alternatively use .setRange() to set both simultaneously. Annotation of value types is supported with both prefixes and suffixes that can be added to the number, e.g. for currency markers or units using .setPrefix() and .setSuffix(), respectively.
Clicking on the up and down arrows on the widget will increase or decrease the value in the widget by an amount, which can be set using .setSingleStep(). Note that this has no effect on the values that are acceptable to the widget.
Both QSpinBox and QDoubleSpinBox have a .valueChanged signal which fires whenever their value is altered. The raw .valueChanged signal sends the numeric value (either an int or a float) while .textChanged sends the value as a string, including both the prefix and suffix characters.
You can optionally disable text input on the spin box line edit, by setting it to read-only. With this set, the value can only be changed using the controls. This also has the side effect of disabling the flashing cursor:
spinbox.lineEdit().setReadOnly(True)
QSlider
QSlider provides a slide-bar widget, which internally works much like a QDoubleSpinBox. Rather than displaying the current value numerically, the slider defines its value by its handle position along the length of the widget. This is often useful when providing adjustment between two extremes, but where absolute accuracy is not required. The most common use of this type of widget is for volume controls.
There is an additional .sliderMoved signal that is triggered whenever the slider moves position and a .sliderPressed signal that emits whenever the slider is clicked:
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My App")
slider = QSlider()
slider.setMinimum(-10)
slider.setMaximum(3)
# Or: widget.setRange(-10,3)
slider.setSingleStep(3)
slider.valueChanged.connect(self.value_changed)
slider.sliderMoved.connect(self.slider_position)
slider.sliderPressed.connect(self.slider_pressed)
slider.sliderReleased.connect(self.slider_released)
self.setCentralWidget(slider)
def value_changed(self, value):
print(value)
def slider_position(self, position):
print("position", position)
def slider_pressed(self):
print("Pressed!")
def slider_released(self):
print("Released")
Run this, and you'll see a slider widget on your screen. Drag the slider to change its value.
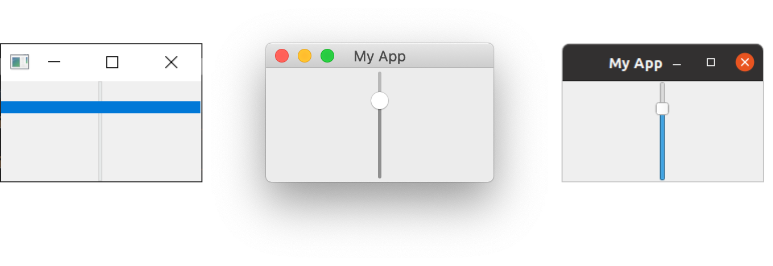 QSlider on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
QSlider on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
You can also construct a slider with a vertical or horizontal orientation by passing the orientation in as you create it. The orientation flags are defined in the Qt.Orientation namespace. For example:
slider = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Vertical)
Or:
slider = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
QDial
Finally, the QDial is a rotatable widget that works just like the slider but appears as an analog dial. This looks nice, but from a UI perspective is not particularly user-friendly. However, they are often used in audio applications as a simulation of real-world analog dials:
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("My App")
dial = QDial()
dial.setRange(-10, 100)
dial.setSingleStep(1)
dial.valueChanged.connect(self.value_changed)
dial.sliderMoved.connect(self.dial_position)
dial.sliderPressed.connect(self.dial_pressed)
dial.sliderReleased.connect(self.dial_released)
self.setCentralWidget(dial)
def value_changed(self, value):
print(value)
def dial_position(self, position):
print("position", position)
def dial_pressed(self):
print("Pressed!")
def dial_released(self):
print("Released")
Run this, and you'll see a circular dial, rotate it to select a number from the range.
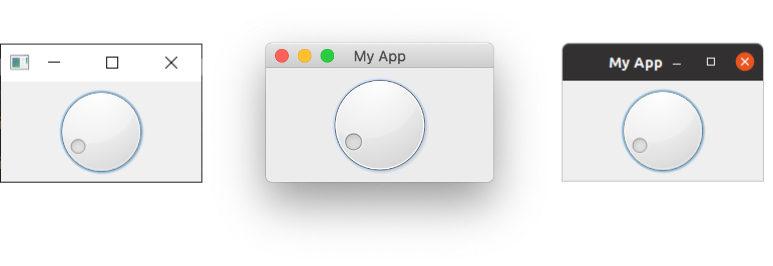 QDial on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
QDial on Windows, Mac & Ubuntu Linux.
The signals are the same as for QSlider and retain the same names (e.g. .sliderMoved).
Conclusion
This concludes our brief tour of the common widgets used in PySide6 applications. To check the full list of available widgets, including all their signals and attributes, take a look at the Qt documentation.
For a more in-depth look at widgets, check out our QComboBox and QPushButton documentation.
Packaging Python Applications with PyInstaller by Martin Fitzpatrick — This step-by-step guide walks you through packaging your own Python applications from simple examples to complete installers and signed executables.

